
Isotope distributions can also be calculated using the Isotopes Calculator in the MS Interpreter tool in the NIST Mass Spectral Database. In Figure 1.2, the scheme of an ionization chamber, ion-source, typically 2005). In all cases, the correct charge states could be determined. Parent ion mass accuracy frequency histograms (in ppm) for all best peptide assignments (red line) and only peptide assignments that predict a methonine sulfoxide (blue bars).

The best solutions in this case form a narrow distribution (Ï = 2 ppm) conforming to the resolution of the mass spectrometer used in the experiment. Jimâs starting material has a monoisotopic mass of 344 (using the most prevalent isotopes), and would drop to 302 if removal of the acetyl group was the only thing that happened. The two most widely used are the peak width definition and the valley definition. There are several ways to define the minimum peak separation ÎM in mass spectrometry, therefore it is important to report the method used to determine mass resolution when reporting its value. "#$ Other techniques worth noting include desorption electrospray ionization (DESI), secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), and more recently easy ambient sonic spray ionization (EASI), 21 which require minimal sample preparation in comparison to MALDI since they do not require the presence of a matrix. The Mass spectra window displays the experimental data (in blue) overlaid with the theoretical matched peaks (in red). Setting mass tolerance too high may compromise the quality of the search.
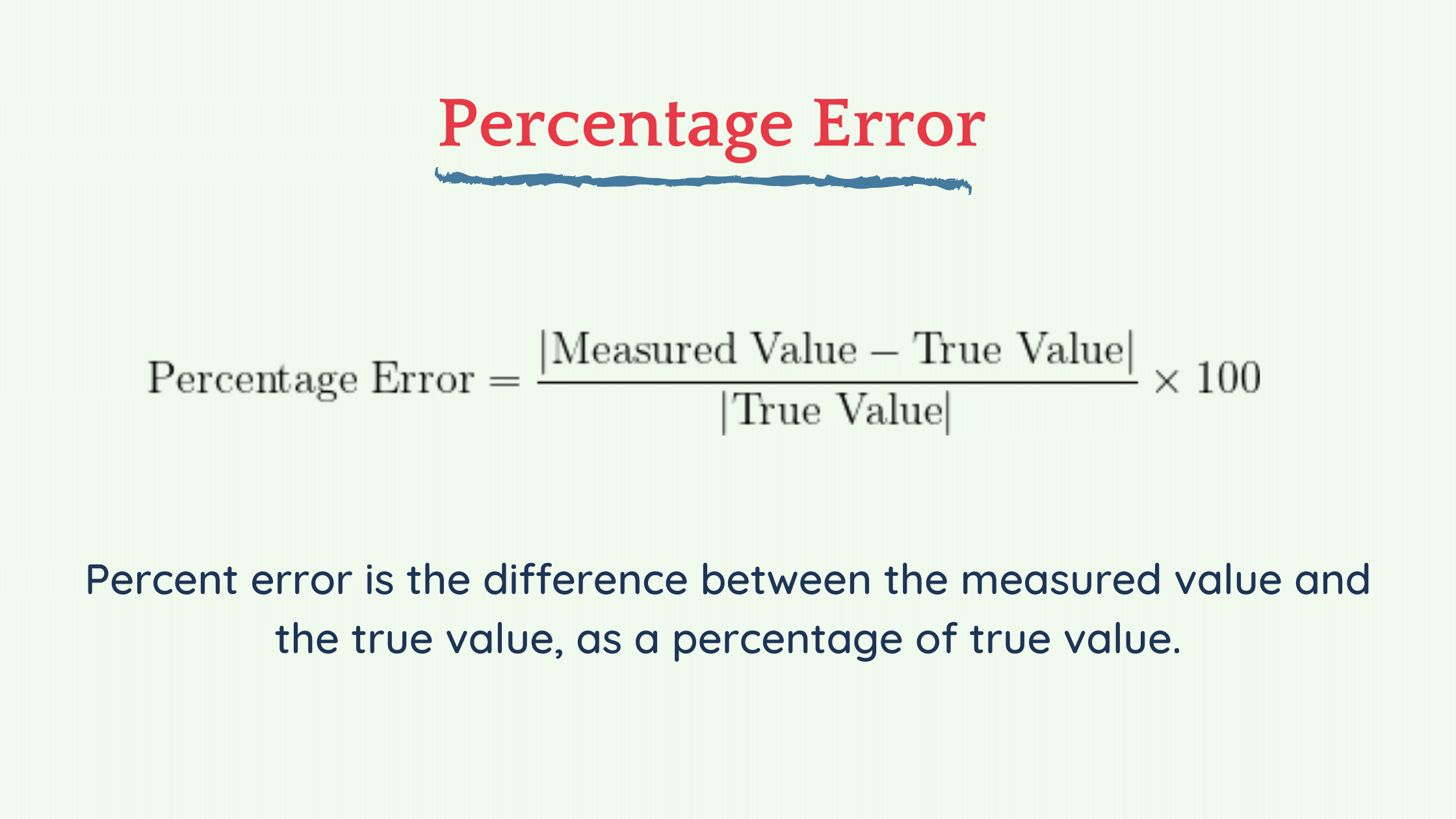
The abbreviation m z is used to denote the dimensionless quantity formed by dividing the mass number of an ion by its charge number. The odd-mass peaks all have a 13 C composition of 1. How is mass defined? The highest-mass isotopic peak has a 13 C composition of 2 because the highest-mass peak is made of all-heavy isotopes, so both carbon atoms must be 13 C. Mass Spectrometry - Mass calculations: mass error and m/z from formula Resolution (mass spectrometry) - Wikipedia In addition, many other types of samples (e.g., carbohydrates, lipids, and polymers) may also be analyzed on the Q-Tof. mass measurement errors of less than 10 ppm with inter-nal calibration. Technology Transition Workshop What is a Mass Spectrometer? 2002 37: 357â∳71. CHAPTER THREE Methane Emission Measurement and Monitoring Methods. As a consequence, two peaks of equal height at m/z 200.0000 and 200.002 cannot be baseline resolved. INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS (I) This ion takes 1.04 × 10 â∵ s to reach the detector. Mass Spec Definitions - Princeton University Standard Addition Example Problem - Widener University Mass tolerance may be entered as the absolute difference in Daltons, or as the fraction of mass in parts-per-million (ppm). Mass spectrometry is a tool that allows researchers to identify and quantify molecules using their known mass. used to calculate the number of compositions for a given oligonucleotide length, and the mass (or m/z)foreach Analysis of raw MS data We discuss in detail when to use each of these approaches in the Library-free search section. Assuming that on a 500 MHz NMR spectrometer the 15N90 pulse length is 35 μsat 60 dB and a higher decibel value means more power for a pulse, what is most likely the power setting for 15N WALTZ-16 decoupling over a 30 ppm bandwidth? Ideally, the mass resolution for accurate mass. Solutions for Oligonucleotide Drug Analysis Form a mass filtering device known as the mass spectrometer. The fragments were analyzed at 70,000 resolving power.


mass Mass accuracy is a key parameter of mass spectrometric performance. Parallel reaction monitoring for high resolution and high mass accuracy quantitative, targeted proteomics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
